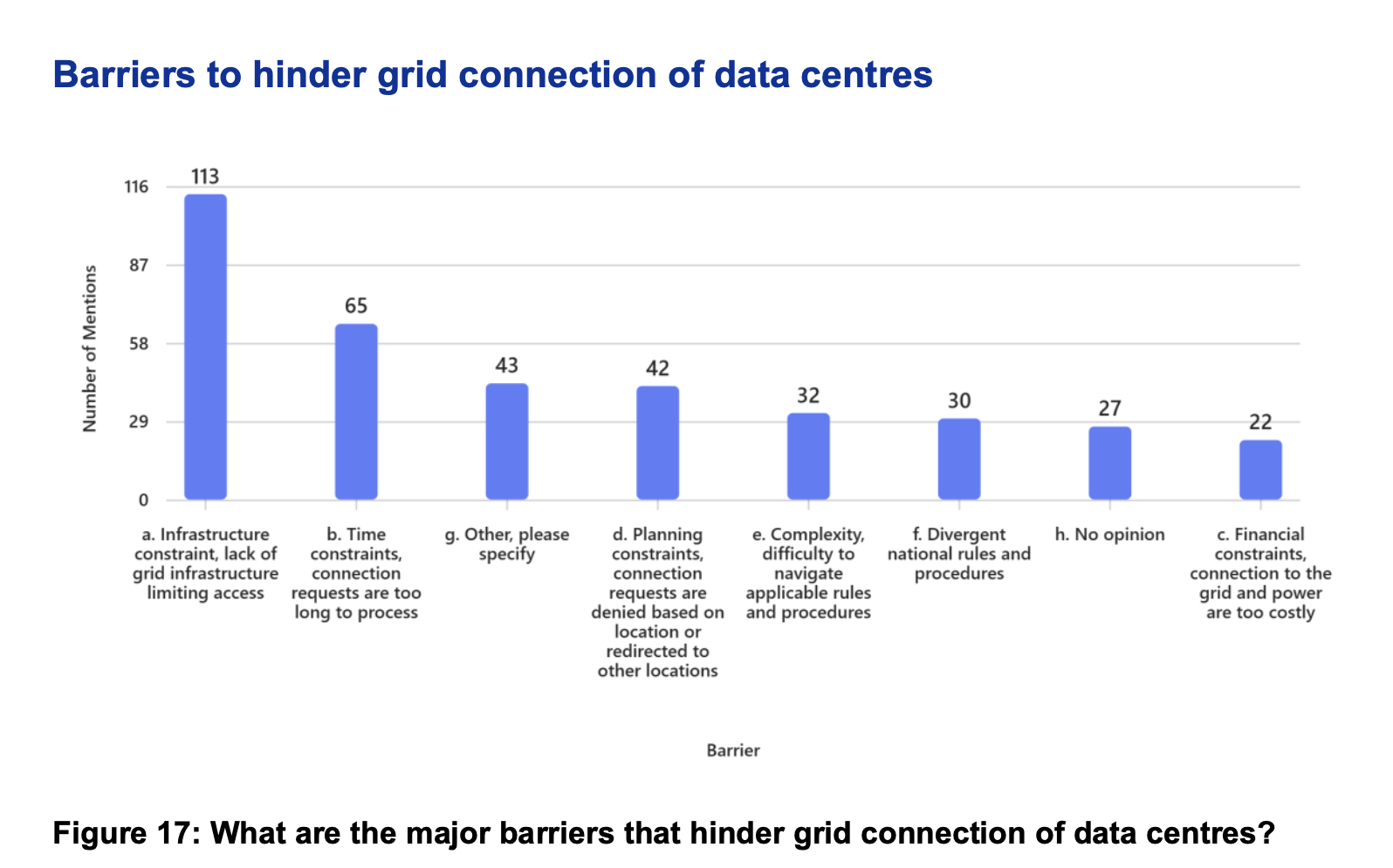

This Pace Global-authored study found greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from coal-generated electrical power to be 92 percent to 194 percent higher than power generated from U.S.-produced LNG in five key international markets.
The study’s findings are in line with recent analysis from the U.S. Energy Information Administration showing that carbon emissions from the power sector hit a 27-year low in April, 2015.
The study provided a granular investigation of emissions during every stage of the LNG lifecycle process, from well head to power generation, and compared those emissions to emissions from coal in five major markets for U.S. LNG exports – Germany, Japan, South Korea, China, and India.